Diabetes Care & its Management
Diabetes is a chronic health issue that affects millions of people worldwide
Effective diabetes care is important for improving the quality of life and preventing complications if you have type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or gestational diabetes. Thankfully, proper management allows those individuals to lead a full and active life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover all aspects of caring for diabetes—from blood sugar monitoring and medications to lifestyle changes and long-term health strategies.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder where your body is either not producing enough insulin, or it cannot use the insulin correctly.
Insulin is a hormone that helps your body utilize glucose (sugar) from food for energy.
When the insulin is ineffective, the blood sugar skyrockets to levels that are dangerous for health and life if left unchecked.
The primary types of diabetes are:
Type 1 Diabetes – An autoimmune form where the body attacks insulin-producing cells.
Type 2 Diabetes – The most common type, often linked to obesity.
Gestational Diabetes – This occurs mainly during pregnancy and usually disappears after giving birth.
The Importance of Diabetes Care
People with diabetes who get regular and personal care can prevent complications such as:
Heart disease and stroke
Kidney disease
Nerve damage
Vision problems
Foot ulcers and amputations
Diabetes control is not just about taking medication. It involves blood sugar control, monitoring health regularly, healthy dietary habits, physical exercise, and counselling on psychological health.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Testing your blood sugar is one of the pillars of diabetes management. When your blood sugar is where it needs to be, you stay as healthy and symptom-free as possible.
Tools include:
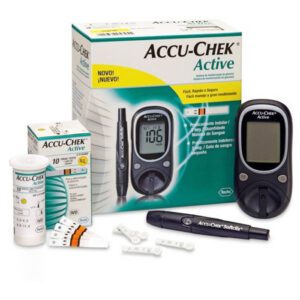
Glucometers—Small devices that measure blood sugar on a daily basis
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)—Use a sensor to give real-time glucose readings
A1C Tests—Measure your average blood sugar level over the last 2 to 3 months
Monitoring allows you to understand how your diet, activity, medication, and stress affect your blood sugar levels.
Diabetes Medications & Insulin Therapy
Medication is an extremely important part of type 2 diabetes treatment and a must for people with type 1.
Common diabetes medications include:
Metformin—the first-line oral medication for type 2 diabetes
SGLT2 Inhibitors—Help the kidneys eliminate sugar via urine
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists—Reduce blood sugar and aid in weight loss
DPP-4 Inhibitors—Help the body keep making insulin
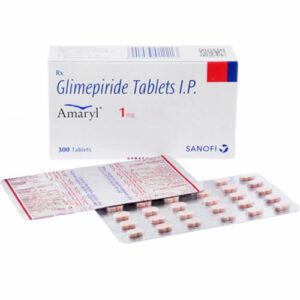
Sulfonylureas—Stimulate insulin production
Insulin—essential for all type 1 diabetics and most advanced type 2 cases
Your doctor will determine whether you need insulin therapy and if so, what type of insulin to use (long-acting, rapid-acting, or mixed). Insulin can be given through pens, syringes, or insulin pumps.
Healthy Eating for Diabetes
Your diet has a major impact on blood sugar control. A diabetes-friendly meal plan includes:
Proteins: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and lean meats
Low-glycemic foods that don’t raise blood sugar
Avoid sugary drinks, refined carbs (like white rice), and processed foods
Carb counting or a personalized plan with a registered dietitian can help significantly.
Physical Activity & Weight Management
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for:
150+ minutes of moderate activity per week (walking, swimming, cycling)
Strength training 2–3 times per week
Daily movement to reduce sitting time
Even small weight loss (5–10% of your body weight) can significantly improve type 2 diabetes and reduce or eliminate the need for medication.
Mental & Emotional Health
Diabetes can take a toll emotionally. Frustration, stress, and burnout are common. Managing mental health is crucial.
Tips:
Join diabetes peer support groups (even online)
Speak with a mental health professional
Try mindfulness activities like yoga or meditation
Routine Medical Checkups
People with diabetes must regularly monitor their health to detect and prevent complications. Your care team might include:
Primary care doctor
Endocrinologist
Diabetes educator
Dietitian
Eye specialist
Foot doctor
Key annual tests include:
A1C test (every 3–6 months)
Kidney function tests
Eye exams
Foot exams
Cholesterol and blood pressure checks
Accessing Diabetes Care Worldwide
Diabetes is a growing global health challenge. When buying diabetes medication online in the USA, UK, or abroad, always use licensed pharmacies with FDA- or MHRA-approved products.
Look for:
Online prescription services
Home delivery of diabetes supplies
Pharmacy support for medication management
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the best treatment for type 2 diabetes?
A: It varies by person but often includes metformin, lifestyle changes, and newer drugs like GLP-1 agonists or SGLT2 inhibitors.
Q: Can diabetes be cured?
A: There’s no cure, but type 2 diabetes can go into remission through diet, exercise, and weight loss.
Q: How often should I check my blood sugar?
A: That depends on your medication and glucose targets. Your doctor will set your monitoring schedule.
Q: Can I travel with diabetes?
A: Yes! With proper planning and by carrying extra supplies, traveling with diabetes is absolutely possible.
Final Thoughts
Managing diabetes is a lifelong journey, but it doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. With the right support, resources, and understanding of your condition, you can live a healthy, balanced, and fulfilling life.